In the rapidly evolving landscape of electronics, the importance of selecting the right flexible printed circuit (FPC) cannot be overstated. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the flexible printed circuit market is projected to reach $28.58 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 10.2% from 2020 to 2025. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for lightweight and compact electronic components across various sectors, including consumer electronics, automotive, and medical devices. The ability of FPCs to conform to various shapes and sizes while maintaining high performance is revolutionizing product designs and functionalities.
Dr. Alice Chen, a leading expert in flexible electronics, emphasizes the significance of this technology in modern applications. She states, "Selecting the right flexible printed circuit can drastically influence the performance and reliability of a device; it's not just about compatibility, but also about optimizing design for efficiency." With an array of design considerations—from the selection of materials to the thickness of circuits—making informed choices about FPCs is crucial for project success. As engineers and designers navigate this complex landscape, understanding the nuances of flexible printed circuits becomes vital in achieving innovative and reliable electronic solutions.

Flexible printed circuits (FPCs) are increasingly gaining traction across various industries due to their ability to conform to different shapes and sizes, making them ideal for compact electronic devices. According to a recent industry report, the flexible printed circuit market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.8% from 2022 to 2028, driven by the demand for lightweight and space-saving electronic components. FPCs offer significant advantages in design flexibility, enhanced durability, and reduced weight, making them crucial for applications in consumer electronics, automotive, and medical devices.
When selecting the right flexible printed circuit for your specific project needs, it's essential to consider factors such as trace width, layer count, and material type. High-frequency applications may require specialized materials like polyimide, which can withstand extreme temperatures and provide excellent dielectric properties. Additionally, understanding the application's environmental conditions—like moisture exposure and temperature fluctuations—will help in choosing the right protective coatings and finishes.
**Tips:** Always evaluate your design requirements and consult with manufacturers to understand the best materials suited for your application. Prototyping can also play a critical role; creating a functional model allows you to test your circuit's performance before full-scale production, reducing risks associated with design flaws. Remember that collaboration with experienced PCB fabricators can help streamline the design process and ensure quality.
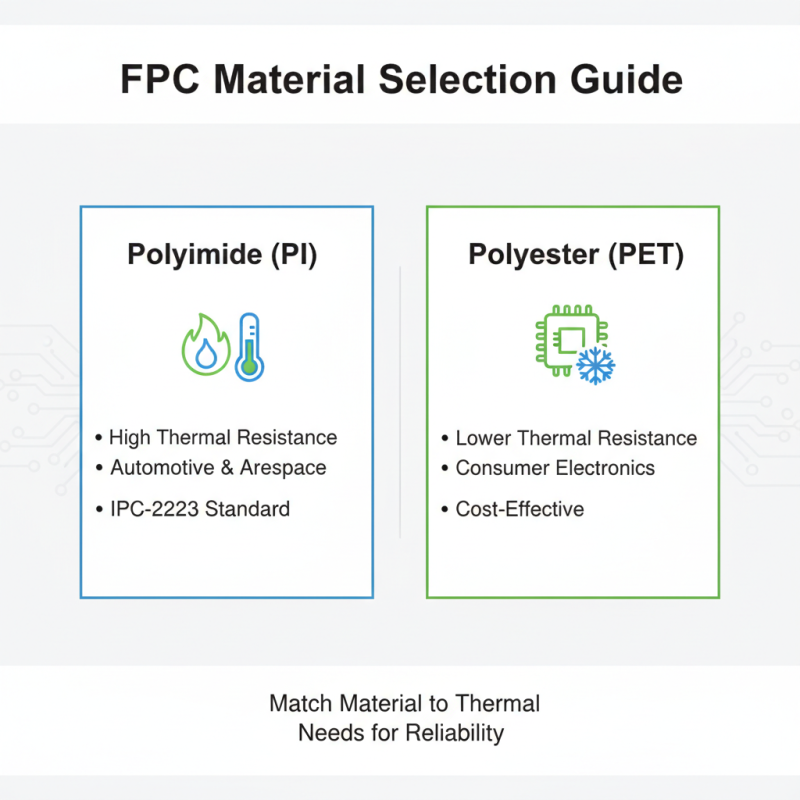
When selecting the right flexible printed circuit (FPC) for your project, understanding key factors is paramount. One of the primary considerations is the material used in the FPC's construction. Common materials like polyimide and polyester offer different thermal and electrical performance characteristics. According to the IPC-2223 standard, polyimide circuits can withstand higher temperatures, making them an optimal choice for applications in high-stress environments like automotive electronics and aerospace technology. It’s essential to analyze the specific thermal requirements of your application to ensure longevity and reliability.
Another critical factor is the circuit design and dimensions. The complexity of the circuit should align with the technical capabilities of the manufacturer. A report by Research and Markets highlights that the flexible printed circuit market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 12% from 2021 to 2026, driving advancements in design technologies. When designing your circuits, take into account the need for miniaturization and the potential for multi-layer configurations, which can significantly improve functionality in limited spaces. This consideration not only enhances performance but can also impact the overall cost-effectiveness of the project. Balancing these factors can lead to a more successful FPC implementation tailored precisely to your needs.
When selecting materials for flexible printed circuits (FPCs), understanding the pros and cons of various options is crucial for achieving optimal performance in your project. One common material is polyimide, known for its excellent thermal stability and mechanical properties. It can withstand extreme temperatures, making it suitable for applications in harsh environments. However, polyimide can be relatively expensive compared to other materials, which may be a consideration for budget-sensitive projects.
Another popular choice is polyester, which is more affordable than polyimide and offers good flexibility and tensile strength. Polyester films can be easier to process, allowing for quicker production timelines. However, one notable drawback is its lower thermal tolerance, limiting its use in high-temperature applications. Additionally, it may not perform as well in terms of dielectric properties, which could affect the circuit’s signal integrity in sensitive electronic applications. Choosing the right material ultimately depends on the specific requirements of your project, including environmental conditions, mechanical stresses, and budget constraints.
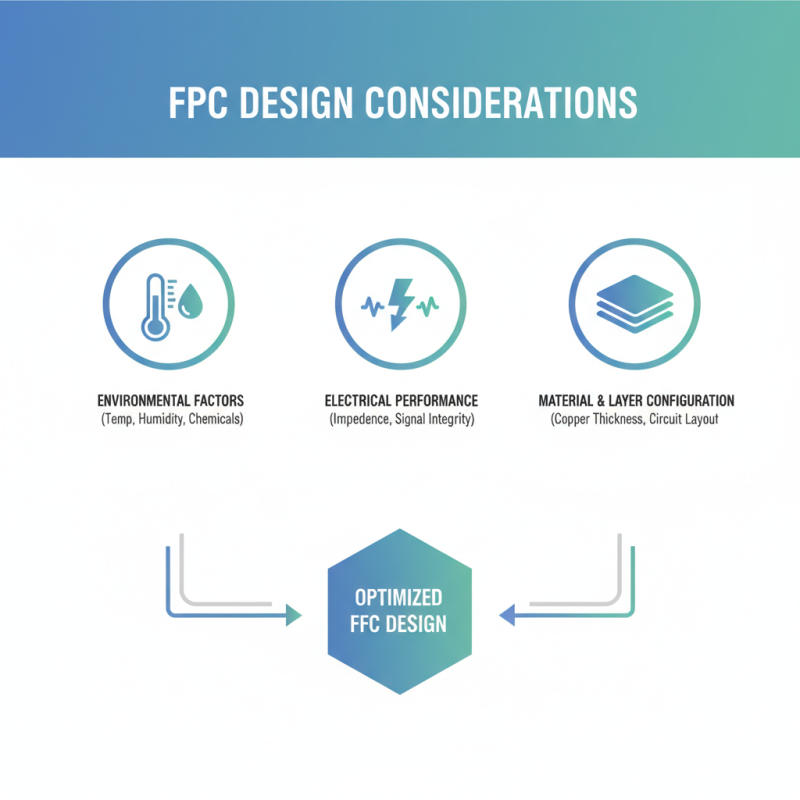
When embarking on a flexible printed circuit (FPC) project, several key design considerations should guide your decisions. First, the application requirements must be thoroughly analyzed. Understanding the environmental factors—such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals—will inform the choice of materials and configurations. Additionally, consider the electrical performance needed; factors like impedance, signal integrity, and power consumption are crucial in determining the thickness of the copper layers and the overall design of the circuit.
Another vital aspect is the dimensional constraints and the physical layout of the FPC. Ensuring that the circuit fits seamlessly into the intended device requires careful planning of bend radii and dimensions to avoid stress concentrations. Alongside this, the assembly process is equally important; whether the circuit will be surface-mounted or integrated into a more complex assembly can influence the design choices. Leveraging simulations and prototypes can further refine your design, mitigating risks associated with manufacturing and integration challenges in the final product.
When selecting a flexible printed circuit (FPC) for your project, one of the most critical factors to consider is the balance between cost and performance. Performance encompasses various aspects such as durability, flexibility, conductivity, and design complexity. While high-performance materials may offer superior characteristics, they often come at a premium price. It’s essential to assess how these performance traits align with the specific demands of your project. For example, if your application requires high reliability in a compact design, the investment in a more advanced FPC might be justified despite higher costs.
On the other hand, cost constraints are inevitable in many projects. Opting for a lower-cost solution without a thorough evaluation might lead to performance issues down the line, potentially impacting the overall functionality and longevity of the final product. Therefore, a strategic approach is necessary. Conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis helps identify the most cost-effective materials and processes that still meet the required specifications. By aligning your project needs with a careful consideration of both performance and budget, you can achieve a balanced solution that maximizes value without compromising quality.
| Parameter | Flexible Printed Circuit Option A | Flexible Printed Circuit Option B | Flexible Printed Circuit Option C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polyimide | PET | Polyester |
| Thickness | 0.1 mm | 0.2 mm | 0.15 mm |
| Minimum Trace Width | 0.075 mm | 0.1 mm | 0.085 mm |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to 125°C | -20°C to 85°C | -40°C to 105°C |
| Cost per Unit | $0.50 | $0.35 | $0.45 |
| Flexibility | High | Medium | High |