Circuit board assembly is a crucial process in the electronics industry. It involves assembling various electronic components onto a circuit board, forming a functional device. Understanding this process helps in grasping how electronic devices operate.
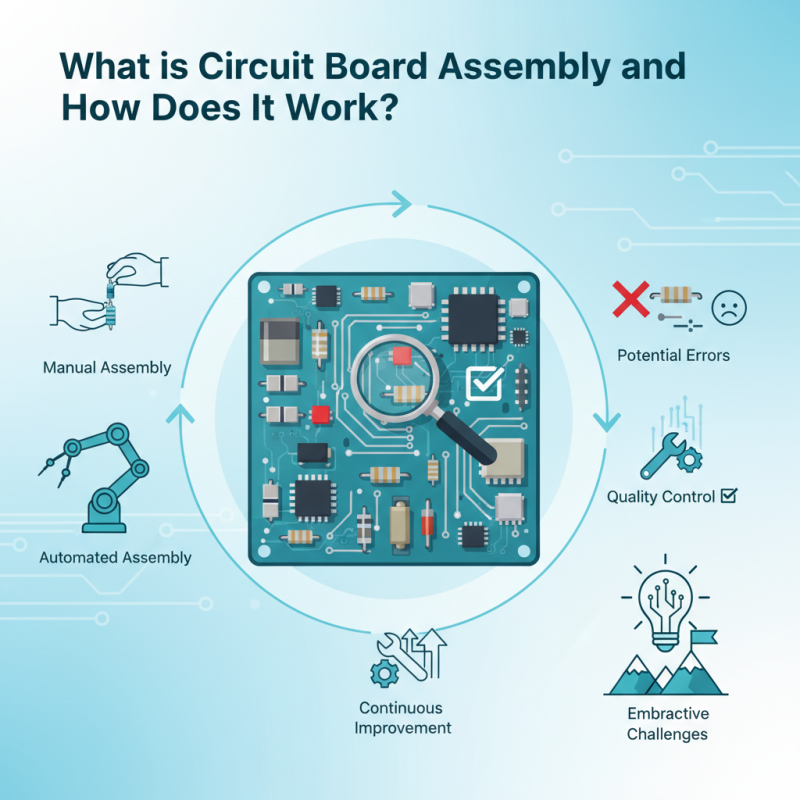
During circuit board assembly, components like resistors, capacitors, and microchips are carefully placed. Each part plays a unique role in the final product. The assembly can occur manually or with automated machines. However, human error can sometimes lead to issues. For example, misplacing a component can cause the device to malfunction.
Attention to detail is vital in circuit board assembly. Quality control measures help ensure the reliability of the devices. Despite these measures, problems may still arise. Continuous improvements are necessary for better outcomes. Embracing challenges can lead to innovative solutions in the industry.
Circuit Board Assembly, often referred to as PCB assembly, is a crucial part of electronic manufacturing. It involves the process of soldering electronic components onto a printed circuit board (PCB). This process is essential for creating functional electronic devices. Each PCB serves as a foundation for various electronic elements. These elements include resistors, capacitors, and microchips.
The importance of PCB assembly lies in its role in modern technology. Every smartphone, computer, and appliance depends on high-quality PCBs. A poorly assembled circuit board can lead to device malfunctions. This can be costly for manufacturers and frustrating for users. Proper assembly ensures the reliability and efficiency of electronic devices. It influences overall performance and longevity. However, challenges persist in achieving perfect assembly. Human errors and equipment malfunctions can occur. These issues highlight the need for continuous improvement in assembly techniques and quality control.
In essence, understanding Circuit Board Assembly is vital. It impacts not just manufacturing but also the end-user experience. As technology evolves, the demand for efficient and reliable PCB assembly grows. Recognizing its significance will help in addressing potential pitfalls in the assembly process. The industry's focus should always be on enhancing accuracy and proficiency in PCB construction.
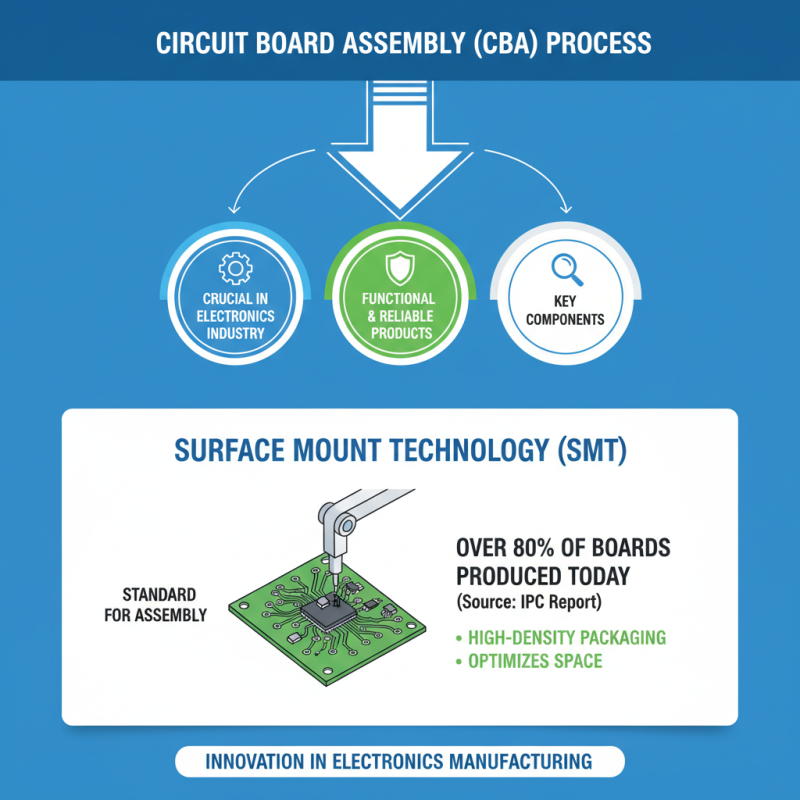
The process of circuit board assembly (CBA) is crucial in the electronics industry. It involves several key components that ensure the final product is functional and reliable. One major component is surface mount technology (SMT), which has become the standard for assembling circuit boards. According to a report by IPC, SMT accounts for over 80% of the boards produced today. This method allows for high-density packaging of components, optimizing space on the board.
Another essential element is through-hole technology (THT). Although used less frequently now, it is still vital for specific applications that require durability. THT provides robust connections which are necessary for high-stress environments. A recent market analysis indicated that combined, SMT and THT account for a majority of circuit board connections, emphasizing their importance in the assembly process.
Despite advancements, the CBA process faces challenges. Quality control remains a critical issue. A study by the International Electrotechnical Commission revealed that about 30% of CBA defects are related to soldering issues. This emphasizes the need for rigorous inspection methods. Continuous improvement should be a goal within the industry. Implementing automated inspection systems can reduce defects significantly. Yet, many companies still rely on manual processes, leaving room for error.
Circuit board assembly (CBA) involves multiple steps that ensure the reliable functioning of electronic devices. The process begins with designing the circuit board layout. This layout must consider component placement, trace routing, and power distribution. Designers often make mistakes during this phase. It's easy to overlook a critical component or create confusing layouts. Testing the design before manufacturing can reduce such issues.
Next comes the process of sourcing components. It’s essential to choose quality parts that meet the design specifications. However, delays in procurement can lead to rushed decisions, resulting in subpar components. Once materials are available, the assembly begins. Techniques vary from manual soldering to automated assembly. Each method has its pros and cons. Manual assembly may be prone to human error, while automation requires precise calibration.
After assembly, the board undergoes inspection and testing. This step is vital for ensuring each connection works properly. Yet, not all defects are immediately visible. Inspectors sometimes miss soldering flaws or misplaced components. Continuous improvement and feedback loops are crucial to refine the assembly process and enhance product reliability. Regular reviews of each step can lead to better practices and higher quality in future assemblies.
Circuit board assembly is a complex process that involves multiple techniques to create functional electronic devices. One common method is surface mount technology (SMT).
SMT places components directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). This technique allows for a compact design and efficient use of space.
However, achieving precision with SMT can be challenging. Any misalignment can lead to circuit failures.
Another technique is through-hole technology. This method involves inserting component leads into holes on the PCB. After insertion, the leads are soldered on the opposite side.
While this technique is reliable, it can result in larger, bulkier boards. Moreover, the assembly process can be time-consuming.
It often requires careful manual work, increasing the chances of error.
Reflow soldering is also prominent in circuit board assembly. This involves heating the solder paste to create solid connections between components and the PCB.
Troubles can arise if the temperature isn’t controlled accurately; cold solder joints may form unexpectedly.
Each technique in circuit board assembly offers unique benefits and challenges. Understanding these intricacies can enhance the overall design and performance of electronic products.
Quality control is essential in circuit board assembly. An estimated 70% of electronic failures originate from PCB assembly errors. These range from misplaced components to soldering faults. Effective quality control can drastically reduce these issues.
Standard measures include visual inspections during production. Automated optical inspection (AOI) is a key technology used to catch defects. A report from the IPC indicates that AOI can improve defect detection rates by up to 80%. However, human oversight remains crucial. Even with automation, errors can slip through.
Additionally, in-process testing is vital. Many manufacturers opt for flying probe testers. These devices check connections while the board is still in production. This method can identify issues early, but it requires skilled operators. Errors can occur if the testers are improperly calibrated. Addressing these challenges is a continuous process that many in the industry are still navigating.