Circuit board manufacturing is a critical process in the electronics industry, serving as the backbone for a vast array of devices that power our modern world. From smartphones to computers, medical devices to automotive systems, circuit boards are essential for connecting various electrical components and facilitating communication between them. This process involves intricate design, precision fabrication, and rigorous testing, ensuring that each circuit board meets the necessary performance and reliability standards.
At its core, circuit board manufacturing encompasses several stages, including material selection, layering, etching, and soldering. Each of these steps is integral to producing high-quality circuit boards that can handle the demands of today's advanced technologies. As innovations in electronics continue to evolve, the techniques and materials used in circuit board manufacturing must also adapt, allowing for smaller, more complex, and more efficient designs.
Understanding how circuit board manufacturing works not only highlights the technical aspects of producing these essential components but also sheds light on the broader implications for industries reliant on electronic devices. By delving into the intricacies of this manufacturing process, we can appreciate the craftsmanship involved and its impact on the overall functionality and performance of electronic systems.

A circuit board, also known as a printed circuit board (PCB), is a crucial component in most electronic devices. It serves as the foundation for connecting various electronic components, such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits. These boards are typically made of non-conductive materials, like fiberglass or plastic, with conductive pathways etched onto their surfaces to facilitate the flow of electricity. This allows for effective communication between different parts of a circuit, ensuring that devices operate smoothly and efficiently.
When exploring circuit board manufacturing, it is essential to consider a few key tips. First, always prioritize quality materials in the manufacturing process. High-quality substrates and conductors can significantly enhance the durability and performance of the circuit board. Second, aim for precision in the etching and design process. Accurate layouts can prevent faults that might disrupt the entire electronic system. Lastly, ensure thorough testing and inspection at various stages of production to identify and rectify any issues before the boards are deployed in final products.
Understanding what a circuit board is and how it functions can greatly benefit anyone involved in electronics, whether in design, manufacturing, or end-use. By recognizing the importance of quality and precision in circuit board creation, manufacturers can produce reliable products that meet the increasing demands of modern technology.

Circuit boards, or printed circuit boards (PCBs), are essential components in electronic devices, serving as the backbone for electrical connections and functionality. A standard circuit board comprises several key elements that work in unison to enable complex interconnections. At the heart of any PCB is the substrate, typically made from materials like fiberglass or epoxy resin, which provides a stable foundation for the circuit. The conductive pathways, usually made of copper, are etched onto the substrate to form the necessary electronic connections among components. According to a recent industry report by IPC, the global PCB market is projected to reach approximately $76.07 billion by 2025, highlighting the critical role these components play in modern technology.
In addition to the substrate and conductive pathways, circuit boards contain various other components, including resistors, capacitors, diodes, and integrated circuits. These components are mounted on the board through various methods, such as surface-mount technology (SMT) or through-hole technology. A report from MarketsandMarkets indicates that the SMT sector alone is expected to exceed $7.6 billion by 2025, driven by the increased demand for miniaturization in electronics. Each component is carefully selected and optimized based on the desired electrical characteristics, and the precise arrangement of these components is vital for the overall performance and reliability of the device. As technology advances, the integration of more complex components onto smaller boards will continue to push the boundaries of circuit board manufacturing.
The circuit board manufacturing process is a complex sequence of steps that transforms raw materials into functional electronic components. It begins with the design phase, where engineers create the schematic and layout of the circuit board using specialized software. This blueprint includes the arrangement of components and the routing of electrical pathways, ensuring optimal performance for the intended application.
Once the design is finalized, the manufacturing process begins with the preparation of base materials, typically layers of fiberglass or epoxy resin. These materials are coated with a thin layer of copper, which is then etched to form the circuitry. Through a combination of photolithography and chemical processes, the design is transferred onto the board, revealing the intricate paths that will carry electrical signals. After etching, additional steps include drilling holes for component leads and plating for better connectivity.
The assembly phase follows, where components such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits are mounted onto the board. This can be accomplished through automated machines or manual labor, depending on the production scale. Soldering is essential at this stage to ensure solid electrical connections, often using techniques like wave or reflow soldering. Finally, the finished circuit boards undergo rigorous testing to verify functionality and quality before they are packaged for distribution, ready to be integrated into various electronic devices.
| Step | Description | Typical Materials Used | Key Equipment | Cycle Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Design and Layout | Software files (Gerber files) | CAD Software | 1-2 weeks |
| 2 | Material Preparation | Copper clad laminate | Cutting machine | 1 day |
| 3 | Etching | Copper | Etching machine | 1-2 days |
| 4 | Drilling | Fiberglass and resin | Drilling machine | 1 day |
| 5 | Plating | Copper, nickel, gold | Plating tank | 1-2 days |
| 6 | Solder Mask Application | Solder mask ink | Solder mask applicator | 1 day |
| 7 | Silkscreen Printing | Silkscreen ink | Silkscreen printer | 1 day |
| 8 | Assembly | Components (resistors, capacitors, ICs) | Reflow oven, soldering tools | 2-5 days |
| 9 | Testing | Testing equipment | Automated test systems | 1-3 days |
| 10 | Packaging and Shipping | Packaging materials | Packing equipment | 1-2 days |
Quality control in circuit board production is a critical aspect that ensures the reliability and performance of electronic devices. According to a recent report by the IPC (Association Connecting Electronics Industries), nearly 70% of all electronic device failures can be traced back to circuit board issues. This highlights the importance of stringent quality control measures throughout the manufacturing process, which typically involves multiple stages, including design validation, material inspection, fabrication, and assembly.
During the fabrication phase, quality control processes such as Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) and X-ray inspection are employed to detect defects like misalignments, shorts, and opens. Reports indicate that implementing these technologies can reduce defect rates by up to 30%. Additionally, the use of statistical process control (SPC) techniques allows manufacturers to monitor production processes in real time, facilitating immediate corrective actions when deviations occur. This proactive approach not only enhances product quality but also optimizes manufacturing efficiency, leading to significant cost savings.
Final testing is equally vital, where advanced methods such as Flying Probe Testing and In-Circuit Testing are utilized to ensure that all components function correctly before the circuit boards are shipped. According to industry studies, properly conducted final tests improve product reliability and reduce return rates by over 20%, demonstrating the crucial role quality control plays in delivering high-performance circuit boards to the market.
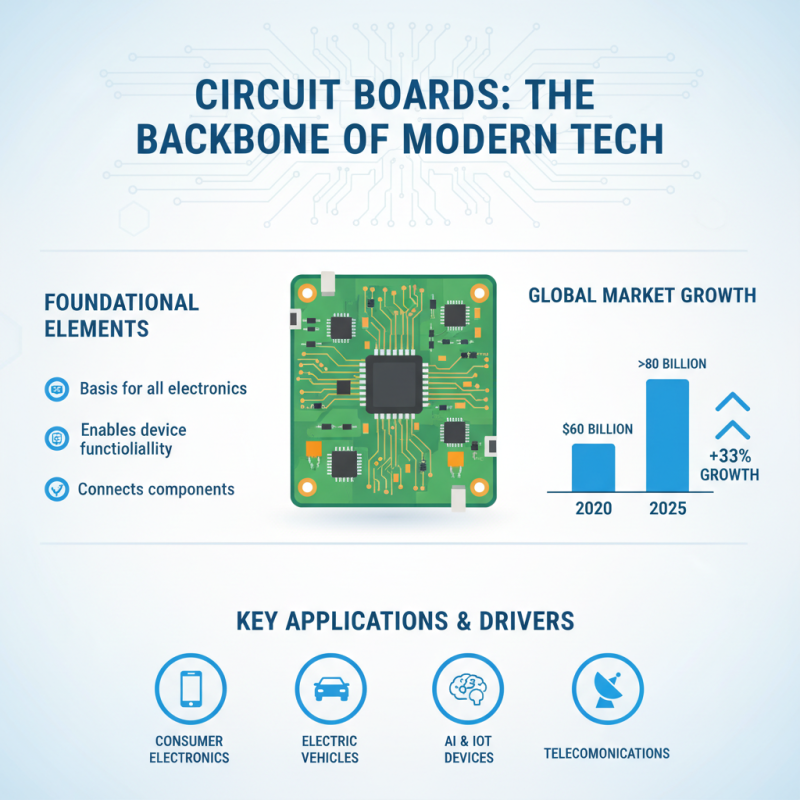
Circuit boards are foundational elements in modern technology, serving as the backbone for a plethora of electronic devices. Applications of circuit boards span across various industries, including telecommunications, automotive, healthcare, and consumer electronics. According to a report by ResearchAndMarkets, the global printed circuit board (PCB) market was valued at approximately $60 billion in 2020 and is expected to reach over $80 billion by 2025, driven by the increasing demand for consumer electronics and the development of advanced technology such as electric vehicles and IoT devices.
In the telecommunications sector, circuit boards are integral to mobile devices, enabling high-speed data transmission, processing power, and connectivity. Similarly, in the automotive industry, PCBs facilitate the functioning of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), infotainment systems, and electric power distribution. The healthcare sector has also seen significant advancements, with circuit boards being utilized in medical devices for diagnostics and patient monitoring. The demand for miniaturized and multi-functional circuit boards in these applications underlines their critical role in modern technology, as they not only enhance performance but also contribute to the overall efficiency and efficacy of electronic products.
As technology continues to evolve, the applications of circuit boards are expected to expand further, incorporating innovations such as flexible and 3D PCBs that cater to emerging technological demands. This trend illustrates the ongoing importance of circuit board manufacturing in supporting the future landscape of electronics across various sectors.