Circuit board fabrication is a fundamental process in the electronics industry. It transforms designs into functional electronic devices. A circuit board serves as a backbone for components like resistors and capacitors. Without it, devices would lack organization and connectivity.
This process involves several steps, including design, etching, and layering materials. Each step requires precision and expertise. Manufacturers face challenges, such as material defects and design flaws, that can lead to failures. Thus, circuit board fabrication must be meticulously executed to ensure reliability.
Moreover, as technology evolves, there is more pressure to create smaller and more efficient boards. This pushes engineers to continually improve fabrication methods. The quest for perfection is ongoing. Despite advancements, imperfections still arise, leading to the need for constant review and refinement in the production process. Circuit board fabrication remains a vital force in driving innovation in electronics.
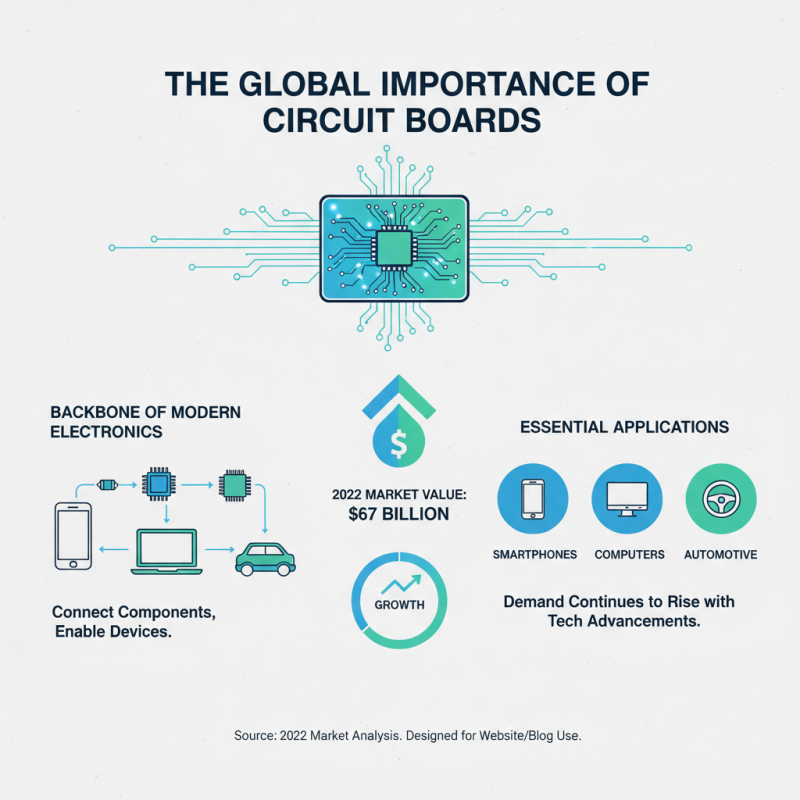
Circuit boards are the backbone of modern electronics. They connect components and allow devices to function efficiently. In 2022, the global printed circuit board market was valued at $67 billion, showcasing its significance. As technology advances, the demand for circuit boards continues to rise. They are essential in smartphones, computers, and automotive applications.
The PCB manufacturing process must be precise. Minor mistakes can lead to significant issues in device performance. In a report by ResearchAndMarkets, the failure rate for poorly fabricated PCBs can exceed 10%. Engineers constantly seek improvement in materials and processes. Suitable materials can enhance durability and reduce electromagnetic interference.
**Tip:** When choosing materials for circuit boards, consider thermal conductivity. This factor helps in managing heat, ensuring longevity and efficiency.
PCB fabrication plays a critical role in IoT devices as well. Effective circuit designs can lead to reduced space and increased functionality. However, it’s vital to balance complexity and cost. Not all innovative designs lead to better performance.
**Tip:** Regularly review and audit your PCB designs. This practice can help identify areas for improvement and prevent costly errors.
Circuit board fabrication is a crucial process in the electronics industry. It involves several key materials, each performing a specific function. The most common base material is FR-4, a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate. FR-4 has excellent mechanical properties and electrical insulation, which is essential for high-performance circuits.
Copper is another vital component. It is used for conductive pathways. The integration of copper layers allows electrical signals to travel efficiently. According to industry reports, the global demand for copper in electronics is expected to rise by 6% annually. However, sourcing high-quality copper can be challenging. It’s essential to ensure that the copper is pure and properly treated.
Tips: Always verify the specifications of materials before use. This step can save time during the fabrication process. Also, consider using alternative materials where appropriate. Some newer composites offer better performance but might require more research. Fabrication can be complex, and occasionally, errors occur. Many small firms often struggle to meet the high standards of material quality. This is an area for growth and improvement. Proper training and awareness can minimize such issues.
| Material Type | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| FR-4 | A widely used flame-retardant glass-reinforced epoxy laminate. | Standard PCBs for consumer electronics. |
| CEM-1 | Composite epoxy material made of paper and epoxy resin. | Low-cost, single-sided boards. |
| Aluminum | Metal core PCBs used for heat dissipation. | High-power applications like LED lighting. |
| Polyimide | Temperature-resistant material used in flexible circuits. | Aerospace and medical devices. |
| Copper | Conductive metal used for traces and pads. | Every PCB as the main conductor of electricity. |
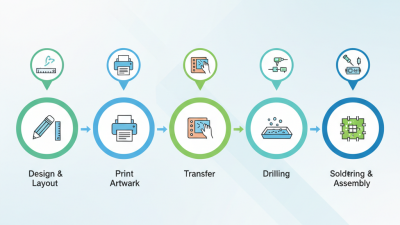
The production of circuit boards is a complex and vital process in electronics. It begins with design and layout. Engineers use software to create schematics and determine connections. This step is crucial to ensure functionality. Next, a prototype may be made. This helps identify errors early on. Sometimes, mistakes occur at this stage, leading to costly revisions.
After the design is solidified, materials are chosen. Copper and fiberglass are common choices. Thin layers are expertly bonded together. This requires precision and care. Any misalignment can cause electrical failures. The etching process then removes unwanted copper, leaving only the desired pathways. This is a delicate task, where over-etching can ruin the board.
Finally, components are soldered onto the circuit board. This requires skill and attention to detail. Even a small error can lead to significant issues later. Quality testing follows. Boards are scrutinized for defects. Sometimes, this process reveals flaws that were initially overlooked. Each step in circuit board production is interconnected. A failure at any point can lead to larger problems in the product lifecycle.
The chart above illustrates the annual production volume of circuit boards from 2018 to 2023. As seen, there has been a steady increase in production over the years, reflecting the growing demand for electronic devices and advancements in technology.
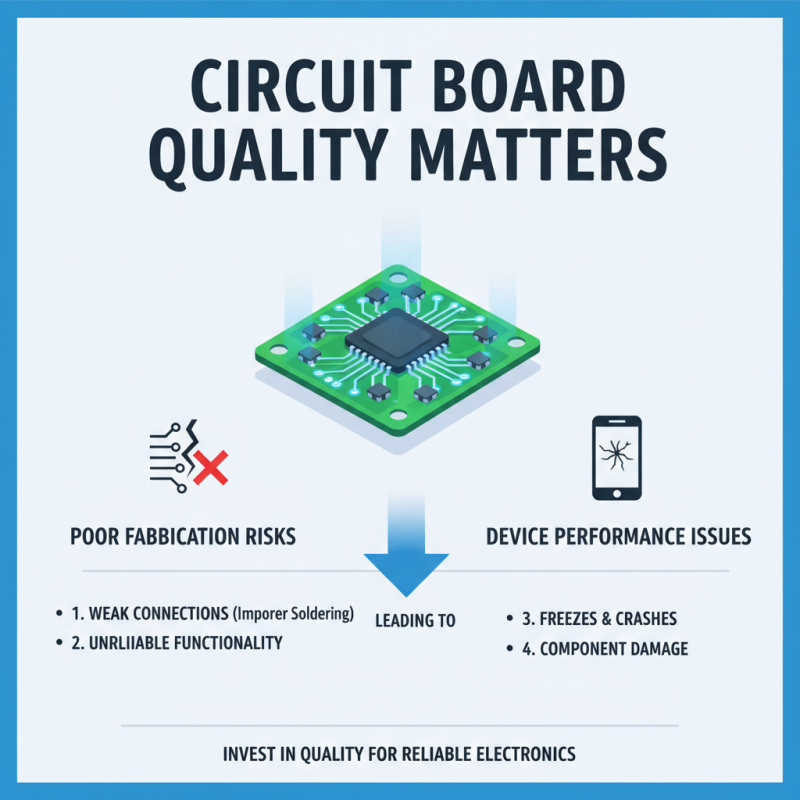
The quality of circuit boards can significantly influence device performance. A poorly fabricated board may lead to electronic failures. For instance, improper soldering can cause weak connections. This results in unreliable functionality. Devices may freeze, crash, or even damage components.
High-quality circuit boards ensure electrical signals travel effectively. This enhances speed and responsiveness. Delays in signal transmission can frustrate users. Additionally, poor heat dissipation may lead to overheating. Over time, this can degrade components.
Manufacturers often overlook the nuances of circuit board design. They may use cheaper materials to cut costs. This can backfire, leading to skyrocketing repair expenses and low customer satisfaction. Striking a balance between cost and quality remains a challenge. It's essential to focus on reliable production processes.
As the electronics industry evolves, circuit board technology faces rapid transformations. Research shows that the global circuit board market is expected to reach $85 billion by 2027, driven by innovations in IoT and AI. This growth comes with challenges, including the need for faster production cycles and reduced costs. Manufacturers must adapt quickly to stay competitive.
Emerging trends highlight the shift toward flexible and printed circuit boards. These designs open up new possibilities for compact and lightweight electronics. However, producing such advanced designs often leads to complex manufacturing processes. Reports indicate that about 20% of production is plagued by defects, which can hinder progress. Companies must invest in advanced inspection technologies to ensure quality.
Sustainability is another key trend. The push for eco-friendly materials is growing. The market for green circuit boards is projected to expand by approximately 14% annually. Yet, sourcing these materials can be problematic. Striking a balance between innovation and sustainability remains a challenge for manufacturers. Embracing these trends will shape the future of circuit board fabrication.